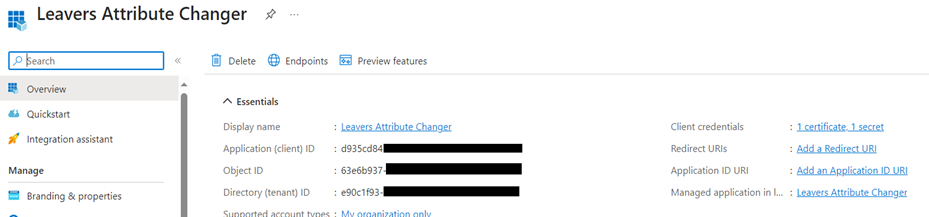
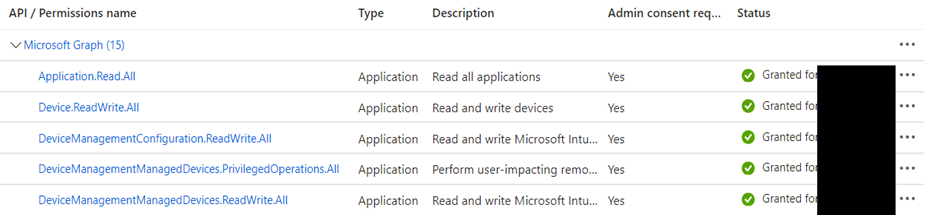
As the digital security landscape continues to evolve, organizations utilizing Microsoft Azure are encouraged to migrate their Identity Protection risk policies to Conditional Access. With Microsoft’s announcement that legacy risk policies in Microsoft Entra ID Protection will be retired on October 1, 2026, now is the crucial time to plan and execute this transition. This guide not only walks you through the migration process but also incorporates Microsoft’s recommended practices for configuring risk policies to protect your organization effectively.
Understanding the Importance of Migration
The retirement of the old risk policies necessitates a shift to a more robust and integrated system. Conditional Access provides a more dynamic framework that allows for real-time assessments and adaptive responses to identity-based threats, making it a superior choice for managing security risks in Azure.
Preparing for Migration
Begin by auditing your existing risk policies in Microsoft Entra ID Protection. Identify which configurations are active and understand their implications to ensure that all critical aspects of your security setup are transitioned without loss of coverage.